The Rise of Solar-Powered HVAC Systems
Solar-powered heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems transform how homeowners and businesses approach climate control. By integrating renewable solar energy with efficient HVAC technologies, these systems drastically reduce both emissions and operational costs.
Behind this surge in popularity is a blend of environmental responsibility and financial motivation. Solar-powered HVAC systems significantly lower energy bills and reduce dependence on traditional power grids, especially in sun-rich regions. Many property owners in coastal and southern areas use Pensacola solar to combine local expertise with cutting-edge technology, ensuring optimal performance and remarkable savings. Favorable government policies, increasing awareness of carbon footprints, and technological advances in solar and HVAC equipment are driving market growth.
Key Takeaways
- Solar-powered HVAC systems cut energy costs, emissions, and grid dependence.
- Core components: solar panels, inverters, batteries, and HVAC units.
- Proper sizing and installation ensure efficiency and compliance.
- Smart technology enables energy monitoring and automated control.
- Regular maintenance and available incentives improve performance and ROI.
- Systems provide long-term savings, increased property value, and sustainable comfort.
Core Components of a Solar-Powered HVAC System
Solar-powered HVAC systems comprise several vital hardware components: solar panels, inverters, batteries, and HVAC units. Each element plays a unique role in ensuring smooth operation and energy efficiency. Photovoltaic solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which is then managed by inverters that convert direct current (DC) into usable alternating current (AC) for HVAC use.
Choosing the right type of solar panel—monocrystalline, polycrystalline, or thin-film—affects the overall system performance. Monocrystalline panels offer superior efficiency and space savings, making them ideal for locations with limited roof area. Batteries, meanwhile, are central to storing excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight, providing greater autonomy and resilience.
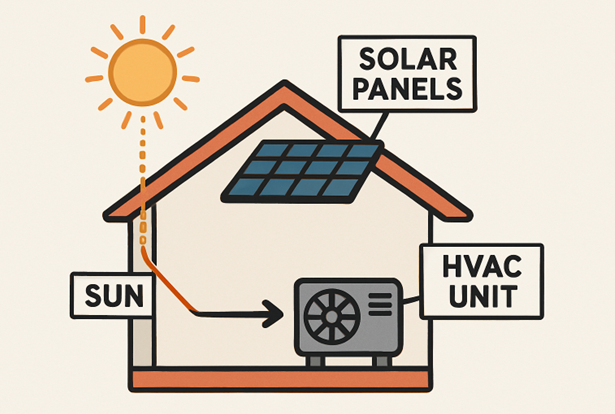
Assessing Energy Demand and Sizing the System
Accurately sizing your solar-powered HVAC system begins with thoroughly assessing your property’s energy needs. Start by calculating the heating and cooling loads, considering not just square footage but also ceiling height, insulation quality, and window exposure. Both residential and commercial buildings require tailored approaches, as energy consumption patterns often differ.
Numerous factors influence energy demand, such as occupancy rates, electronics usage, seasonal temperature fluctuations, and internal heat gains. Tools like load calculators or professional software can help you estimate the HVAC requirements efficiently, ensuring you neither oversize nor underestimate your system.
Factors Affecting System Design and Performance
Geographic location and climate are critical determinants of solar HVAC system design. Communities with abundant sunshine can generate more power year-round, while those in cloudier or northern areas may need increased panel surface area or enhanced battery capacity. Sunlight exposure—how many hours of direct sun your site receives—significantly affects total energy production.
Roof orientation and angle play substantial roles in maximizing solar collection. For optimal results, panels should ideally face south (in the Northern Hemisphere) and be tilted to match your latitude. Enhancing building insulation and implementing energy efficiency measures such as window upgrades or sealing leaks will further reduce HVAC loads, improving comfort and overall system efficiency.
Also read: Fintechasia.net Start Me Up: Financial Innovation in Asia
Installation Best Practices
Partnering with experienced, certified installers ensures your solar-powered HVAC system is set up safely and efficiently. Qualified professionals are adept at site assessment, panel placement, wiring, and system calibration to avoid performance shortfalls. The installation typically includes a site inspection, panel mounting, electrical wiring, inverter and battery connection, and rigorous functional testing.
Compliance with local building codes, electrical regulations, and fire safety standards is essential. Municipal inspection and permitting procedures must be followed closely to guarantee safe operation and preserve eligibility for rebates or incentives.
Integrating Smart Technology
Smart thermostats, IoT devices, and integrated controllers can revolutionize your solar-powered HVAC system. These technologies facilitate precise temperature control, enable automated schedules, and allow for real-time energy consumption monitoring. Homeowners and building managers can access advanced reporting and remote adjustment features via mobile apps or web platforms, further optimizing energy savings. Automation and monitoring help prevent unnecessary energy waste and provide actionable insights for maintenance, early-warning alerts, and system performance benchmarks.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Routine maintenance is crucial to ensuring the long-term reliability of your solar HVAC system. Key practices include regularly cleaning solar panels, checking for obstruction or shading, verifying electrical connections, and monitoring inverter and battery status. It’s wise to schedule professional inspections annually to identify early signs of wear or malfunction.
Common warning signs of system issues may include erratic HVAC performance, unusual noises, reduced energy output, or repeated system resets. While minor troubleshooting—like clearing debris or resetting breakers—can be managed by the owner, persistent or complex issues warrant professional attention.
Financial Incentives and Long-Term Savings
Numerous financial incentives—federal tax credits, local rebates, and utility programs—are available for property owners installing solar-powered HVAC systems. For example, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) provides considerable savings by allowing homeowners to deduct a percentage of installation costs. Local programs can further reduce upfront expenses and shorten payback periods. The long-term savings from solar HVAC systems stem from dramatically lower electricity bills and increased property value. Many users report returns on investment within seven to ten years, with ongoing savings long after.
Making Informed Choices for a Sustainable Future
Designing and installing a solar-powered HVAC system requires thoughtful consideration—from equipment selection and accurate sizing to integrating smart technology and diligent maintenance. As renewable energy innovation accelerates, solar-powered climate control is poised to become the standard for sustainable comfort and significant cost savings. By understanding these best practices and key design considerations, you can make an informed investment that benefits both your finances and the environment for years to come.
See more: Esports News Dualmedia: A Game-Changer for the Industry
